Wired or Fueled? Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering—The Battle of the Giants

Blog / June 20, 2025
Electrical or Mechanical?Electrical or Mechanical Engineering?Mechanical and electrical engineers have quietly shaped the world around us—whether it’s the machines we use, the power we rely on, or the way we travel and communicate. From early industrial machines to today’s satellites and smart systems, their work is everywhere.
Right now, the need for these engineers is growing fast. Electric vehicles, clean energy, automation, and robotics are no longer future trends—they’re part of daily life. And behind all this progress are people who know how to build, wire, design, and solve.
If you're thinking of a career in engineering, B.Tech. in Mechanical or Electrical Engineering are two of the most solid options. These four-year degrees mix theory with hands-on projects and open doors to exciting roles in modern industries.
In this blog, we’ll break down what each branch offers and how to choose the one that fits your interests and career goals.
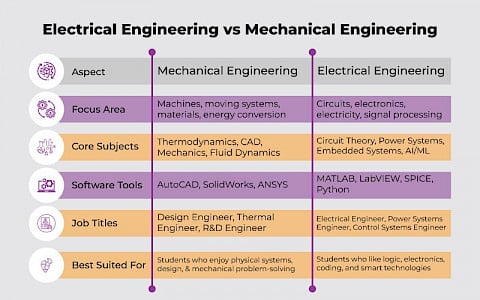
Table of Contents
- Why Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering Face-Off Matters?
- From Force to Function, Driving the World Forward: Mechanical Engineering
- Power that Empowers the World: Electrical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: The Big Showdown
- How Educational Pathways Shape the Engineer You Become
- Which Skills Make You Thrive? Hard and Soft Competencies Explained
- Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Specializations That Set You Apart
- Work Environments, Tools, and Technologies: What a Day in the Life Looks Like
- Credentials That Help You Stand Out in the Industry
- Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Real-World Applications
- Future-Proofing Your Career: Which Discipline Is More Resilient to Automation and AI?
- Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Who Should Choose What?
- Want to Power the World or Fuel Machines? Start Your Journey at Shiv Nadar University (Institution of Eminence)
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering Face-Off Matters?
Choosing between electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering isn’t just about picking a college course. It’s about deciding the kind of future you want to build. You’re at a point where every decision carries weight, and the pressure to “choose the right path” feels like a full-time job.
You're probably asking:
- Which branch has a better job scope?
- Will I earn more as a mechanical or electrical engineer?
- Is one more future-proof than the other?
- Which one suits your interests or skills better?
These are smart questions. And you’re not alone. Every year, lakhs of students in India and their parents wrestle with this choice. Because when you're aiming for B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering or B.Tech. Electrical Engineering, you're not just selecting a stream. You’re shaping the life you’ll live five, ten, or twenty years from now.
From Force to Function, Driving the World Forward: Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is everywhere. From your car’s engine to the wind turbine powering your streetlights, mechanical engineers build the systems that move us.
If you enjoy solving real-world problems with physical things: machines, engines, tools, this is where your curiosity might belong. You’ll study in B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering:
- Thermodynamics
- Strength of Materials
- Fluid Mechanics
- Machine Design
- Robotics and
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Mechanical engineers work at:
- Automotive (Tata Motors, Mahindra)
- Aerospace (ISRO, HAL)
- Manufacturing (L&T, BHEL)
- Biomedical devices (GE Healthcare) and
- HVAC systems and power plants
You might work on:
- Designing aircraft turbines and propulsion systems for the aerospace sector
- Building energy-efficient engines and transmissions for electric vehicles and hybrid systems
- Creating material handling systems like conveyors and automated cranes used in smart factories
- Engineering thermal systems for cooling high-performance electronics or EV batteries
- Optimizing HVAC and renewable energy systems to meet sustainability goals and
- Working on next-gen automotive platforms
If you like hands-on creation and tangible results, this field rewards your mindset. Mechanical engineers are builders, testers, and troubleshooters. You build the moving parts of the world.
Power that Empowers the World: Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering focuses on electricity, circuits, signals, and systems. Think less nuts and bolts, more data and power. The key functions of electrical engineering are: Generation, Transmission, and Distribution of Power.
If you're into tech, communication, clean energy, or digital control, this could be your space. Electrical engineers don’t just design wiring. They power smart homes, electric vehicles, drones, satellites, and AI systems.
You’ll study in B.Tech. Electrical Engineering:
- Circuit Theory
- Control Systems
- Digital Electronics
- Signal Processing
- Power Systems and
- Embedded Systems and IoT
Electrical engineers work at:
- Electronics (Intel, Qualcomm)
- Energy and utilities (NTPC, Siemens)
- Telecom (BSNL, Reliance Jio) and
- Smart tech and automation (ABB, Schneider Electric)
You might work on:
- Designing embedded systems and microchips
- Developing AI-powered navigation and control systems
- Engineering renewable energy infrastructure
- Programming control algorithms for self-driving cars
- Building power electronics used in electric motors, industrial automation, and high-performance computing, and
- Creating signal processing systems for technologies like voice recognition, biomedical devices, and surveillance tools
You take invisible power and make it perform real tasks. This field is always evolving, and so will you.
Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: The Big Showdown
Here's a side-by-side comparison to help you see the big picture between electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering:
|
Aspect |
Mechanical Engineering |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Focus Area |
Machines, moving systems, materials, energy conversion |
Circuits, electronics, electricity, signal processing |
|
Core Subjects |
Thermodynamics, CAD, Mechanics, Fluid Dynamics |
Circuit Theory, Power Systems, Embedded Systems, AI/ML |
|
Software Tools |
AutoCAD, SolidWorks, ANSYS |
MATLAB, LabVIEW, SPICE, Python |
|
Key Industries |
Automotive, Aerospace, Power Plants, Robotics |
Telecom, Electronics, Renewable Energy, Embedded Systems |
|
Example Projects |
Design of aircraft turbines, hydraulic machines |
EV charging systems, IoT devices, AI-integrated microcontrollers |
|
Job Titles |
Design Engineer, Thermal Engineer, R&D Engineer |
Electrical Engineer, Power Systems Engineer, Control Systems Engineer |
|
Growth Rate |
Steady with growth in manufacturing and green energy |
Rising rapidly with AI, automation, and clean energy demand |
|
Top Recruiters |
BHEL, ISRO, Tata, L&T, Ashok Leyland |
Siemens, Schneider Electric, DRDO, General Electric, NTPC, NHPC, Power Grid Corporation of India |
|
Best Suited For |
Students who enjoy physical systems, design, and mechanical problem-solving |
Students who like logic, electronics, coding, and smart technologies |
Both fields are rigorous. Both lead to stable, creative, and high-impact careers. Choosing between B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering and B.Tech. Electrical Engineering isn’t about picking the “better” one. It’s about picking the right one for you.
How Educational Pathways Shape the Engineer You Become
Your engineering journey doesn’t start in a company. It starts in a classroom. And the right classroom makes all the difference. Choosing electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering means more than picking a subject. It means diving into a four-year path that sets up your career, mindset, and how you solve problems.
Let’s break it down.
What B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering Covers
- Engineering Mechanics
- Thermodynamics
- Machine Design
- Manufacturing Processes
- Robotics and Mechatronics
- Fluid Mechanics
- Materials Science
- Applied Mechanics
- Control System
- Kinematics of Machines
- Manufacturing Technology
- Strength of Materials
- Solid Mechanics
- Heat and Mass Transfer, and
- CAD and CAM Tools
You’ll deal with real machines: motors, pumps, turbines, and design systems that make them work better, faster, and safer.
What B.Tech. Electrical Engineering Includes
- Electric Circuits and Devices
- Signal Processing
- Power Electronics
- Embedded Systems
- Control Systems
- Artificial Intelligence and IoT Applications
- Electrical Machines
- Electromagnetism
- Electric Power System
- Analog Electronics
- Digital Electronics
- Computer Programming
- Electric Drives
- Circuit Theory and
- MATLAB, Simulink, etc, tools
You’ll work with circuits, sensors, data systems, and smart devices.
Lab Work and Learning Style
Both paths teach through experiments and projects, but the tools are very different.
- Mechanical labs are physical. Expect machines, tools, cutting fluid, and sparks flying from lathe machines.
- Electrical labs are digital. You'll use oscilloscopes, test benches, simulation software, and microcontrollers.
Which Skills Make You Thrive? Hard and Soft Competencies Explained
Success in electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering depends on more than your grades. Your skillset matters. Here’s how the two fields differ when it comes to what you need and what you’ll gain.
Soft Skills That Matter
- Analytical Thinking – Solve new problems with logic.
- Creativity – Design new devices, not just fix old ones.
- Communication – Present your work in meetings or explain concepts to a team.
- Time Management – Projects and deadlines go hand in hand.
Core Technical Skills
|
Skill |
Mechanical Engineering |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Software Proficiency |
AutoCAD, SolidWorks, ANSYS |
MATLAB, Python, LabVIEW, VHDL |
|
Math Use |
Calculations in kinematics, fluid dynamics |
Signal analysis, data interpretation |
|
Tool Use |
Machines, welding tools, compressors |
Multimeters, soldering kits, simulation software |
|
Design Thinking |
Product modeling, ergonomic designs |
PCB design, logic circuits |
Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Specializations That Set You Apart
Engineering today is more layered than ever. Once you choose between electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering, you’ll face another decision: what to specialize in.
This can shape your job role, salary, and even your ability to work abroad.
Top Specializations in Mechanical Engineering
Robotics & Automation
- Design and control smart machines.
- In-demand in manufacturing and defense.
- Used in robotic arms and self-driving systems.
Thermal and Fluid Sciences
- Work on turbines, heat exchangers, and climate control systems.
- Important in the energy and HVAC industries.
Mechatronics
- Mixes mechanical systems with electronics.
- Used in drones, medical devices, and automation.
Computational Design
- Use software to simulate stress, heat, and motion in product development.
- Crucial in aerospace, automotive, and structural design.
Energy Systems
- Focus on sustainable energy, power generation, and energy efficiency.
- Applied in renewable energy plants and industrial operations.
Biomechanics
- Develop mechanical systems for healthcare and assistive devices.
- Used in prosthetics, orthotics, and surgical tools.
Leading Specializations in Electrical Engineering
Embedded Systems
- Design processors that run your phone, watch, or car.
- Strong demand in consumer electronics and IoT.
VLSI Design
- Work on microchips and integrated circuits.
- Needed in chip manufacturing companies like Intel and TSMC.
Modern Energy Systems
- Work with renewable energy, smart grids, and EVs.
- Focus on sustainable and clean tech.
Power Systems
- Design and manage electricity networks and grids.
- Key to smart cities, renewables, and EV infrastructure.
AI & Machine Learning
- Apply algorithms to optimize electrical systems.
- Used in smart grids, predictive maintenance, and autonomous tech.
Signal & Image Processing
- Interpret sound, images, and video signals.
- Used in communication, security, and healthcare.
Control Systems
- Create stable, automated systems.
- Applied in robotics, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Wireless & Communication Systems
- Work on 5G, satellite, and data transmission.
- Core to modern telecom and network technologies.
Work Environments, Tools, and Technologies: What a Day in the Life Looks Like
Mechanical Engineering: Hands-On and Heavy-Duty
Mechanical engineers often work in manufacturing units, workshops, R&D departments, or testing labs. In companies like L&T, Tata Motors, or ISRO, here’s what your day might include:
- Designing parts on AutoCAD or SolidWorks
- Running stress tests on machines using ANSYS
- Monitoring assembly lines and
- Troubleshooting motors, pumps, or HVAC systems
You’ll work around machines, often loud, hot, and in motion.
Tools You’ll Use Daily:
- CAD Software
- CNC Machines
- Welding and Fabrication Tools
- Laser Cutters and
- 3D Printers
Your routine will mix field visits, design work, and problem-solving on the shop floor.
Electrical Engineering: Powered by Code and Control
If you're leaning toward B.Tech. Electrical Engineering, your work environment will feel more controlled and precise. You’ll likely be in a lab, control room, or office setting, with less grease and more graphs.
In companies like Siemens, Schneider Electric, or Intel, here’s what your day might involve:
- Designing circuits with MATLAB or Multisim
- Programming microcontrollers using Python or C
- Testing sensors and embedded systems, and
- Monitoring power distribution systems
You’ll often work with digital tools, circuit boards, and logic gates.
Core Tools of Daily Use:
- Digital Oscilloscopes
- Simulation Software (PSPICE, LabVIEW)
- Breadboards and PCBs
- IoT Devices and Sensors, and
- Soldering Stations
Some electrical engineers also work on live grids, like those powering metros or data centers. So, safety training is a must.
Key Differences at a Glance
If you prefer building and fixing things with your hands, mechanical fits. If you enjoy coding, precision, and logic boards, electrical may be your thing.
|
Aspect |
Mechanical Engineering |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Primary Setting |
Workshops, plants, testing floors |
Labs, control rooms, R&D units |
|
Key Tools |
CAD, CNC, thermal systems |
MATLAB, circuits, embedded platforms |
|
Physical vs Digital |
Mostly physical systems |
Mostly digital/electronic systems |
|
Workplace Risks |
High heat, mechanical hazards |
High voltage, electronic sensitivity |
Credentials That Help You Stand Out in the Industry
A degree is a strong start. But in a competitive world, extra certifications help you rise faster.
Must-Know Certifications in India
|
Field |
Recommended Certifications |
|
Mechanical |
SolidWorks, AutoCAD, Six Sigma, NDT Level II, CNC Programming |
|
Electrical |
PLC Programming, MATLAB, SCADA, Embedded Systems, Python |
These boost your resume and help with internships, core placements, and higher studies.
GATE Exam
The GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering) is vital if you plan to:
- Pursue M.Tech
- Apply to PSU jobs (NTPC, ONGC, BHEL)
- Go into research or teaching
GATE scores stay valid for three years and are often used by employers to shortlist candidates.
Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Real-World Applications
You’re not just choosing a course. You’re picking where your work will show up in the real world. And the electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering decision shapes what you'll build, fix, or power. Both fields touch almost everything around you: from how your phone charges to how metro doors open and close.
Let’s explore where these careers lead once you leave the classroom.
Where Mechanical Engineering Comes Alive
Mechanical engineers design machines, test systems, and improve how devices perform under pressure. Your projects may include:
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
You’ll design powertrains, cooling systems, and structural components for vehicles and test for strength, weight, and energy efficiency.
Robotics
From industrial robots in automobile factories to prosthetic limbs in healthcare, mechanical engineers design joints, actuators, and the physical framework.
Aerospace Systems
You could help build turbines, propulsion systems, or landing gear that can survive space and speed.
Green Energy Systems
Mechanical minds design wind turbine blades, solar panel support structures, and HVAC systems to reduce energy loss.
Where Electrical Engineering Shapes the Future
Electrical engineers bring intelligence and energy into the equation. You’ll work on:
Smart Grids and Power Systems
You design systems that balance loads, prevent blackouts, and manage renewable integration.
Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
You’ll program control systems, set up GPS, and build the logic that makes machines think and respond.
Consumer Electronics
From PCB layout in smartwatches to signal systems in VR gear, your skills power personal tech.
Medical Equipment
Devices like ECG machines, pacemakers, and remote patient monitors need precision. That’s where you step in.
Future-Proofing Your Career: Which Discipline Is More Resilient to Automation and AI?
AI is everywhere. So what happens to your career if machines take over more work? Let’s look at both sides of electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering from a future-readiness lens.
Mechanical Engineering: At Risk or Evolving?
Some mechanical tasks, like assembly or manufacturing, are already getting automated. But roles that require:
- Human creativity
- Physical prototyping
- System troubleshooting
can’t be replaced easily.
New areas like mechatronics and robotics need mechanical know-how to work with AI hardware.
Electrical Engineering: Aligned with the AI Boom
Electrical engineering is closely tied to:
- Machine learning chips
- IoT networks
- Smart power systems
So demand is rising.
You’ll help build the infrastructure that powers automation, not get replaced by it. Learning tools like Python, TensorFlow, or MATLAB boost your AI compatibility.
Electrical Engineering vs Mechanical Engineering: Who Should Choose What?
Not all choices come from data. Some come from fit. Ask yourself:
- Do you like coding and logic circuits? You’ll feel more at home in electrical engineering.
- Do you prefer physical systems, design, and machines? Mechanical engineering fits your strengths.
There’s no wrong choice. But knowing how you think can point you in the right direction. Let’s compare by thinking styles.
|
Trait |
You Might Prefer |
|
Logical and analytical |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Visual and spatial |
Mechanical Engineering |
|
Passion for electronics |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Love for moving machines |
Mechanical Engineering |
|
Interest in smart tech |
Electrical Engineering |
|
Enjoy building from scratch |
Mechanical Engineering |
Want to Power the World or Fuel Machines? Start Your Journey at Shiv Nadar University (Institution of Eminence)
Whether you're looking at B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering or B.Tech. Electrical and Computer Engineering, Shiv Nadar University offers a robust ecosystem that blends academic depth with real-world readiness.
- Industry-centric curriculum with research depth
- State-of-the-art labs and innovation facilities
- Access to industry-grade simulation software
- Faculty members with Ph.D. degrees from various IITs / universities abroad
- Options to pursue the most in-demand specialization
- Opportunity to undertake research projects under the Opportunities for Undergraduate Research (OUR) program
- Placement assistance backed by strong corporate networks
- Financial aid is available to deserving students who meet the eligibility criteria
Apply now at the School of Engineering of Shiv Nadar University and secure your future.
Conclusion
Choosing between electrical engineering vs mechanical engineering is something that depends on personal interest and career aspirations. Students must always weigh both with respect to their career choices and future prospects.
If you want to pursue B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering or B.Tech. Electrical Engineering from a world-class university, apply now at Shiv Nadar University.
FAQ
Which has better scope in India, electrical engineering or mechanical engineering?
Both have strong scope. Electrical has a slight edge in new-age tech like IoT, AI, and automation.
What is the main difference between B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering and B.Tech. Electrical Engineering?
Mechanical engineering focuses on physical systems and machines. Electrical engineering deals with circuits, signals, and smart technologies.
Can mechanical engineers work in the software or IT field?
Yes, if you pick up relevant skills like coding, data analysis, or automation tools.
What are the job opportunities after B.Tech.?
You can work in core companies, tech firms, startups, research labs, or pursue higher education globally.