Biomedical Engineering vs Biotechnology: Here’s What Recruiters & Experts Say in 2025

Blog / June 17, 2025
Biomedical EngineeringBiotechnologyA cancer drug that targets only the right cells. A bionic arm moved by thought. An edible vaccine grown inside a banana. A heart valve printed from living tissue. From the insulin that saves lives to high-yield crops feeding millions, biology and engineering are now part of everyday essentials.
Behind this progress are two kinds of professionals: biomedical engineers and biotechnologists. One works with cells and molecules. The other builds devices that support life. Both solve big problems, but in very different ways.
With a continuous upsurge in demand across healthcare, biotech, pharma, and sustainable innovation, choosing between biomedical engineering vs biotechnology has become more about personal choices and interest than just an academic decision.
Let’s decode the difference.
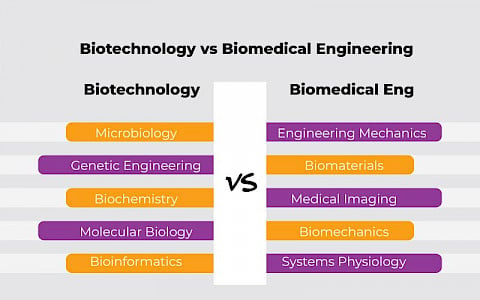
Table of Contents
- Why Biomedical Engineering vs Biotechnology Comparison Matters More Than Ever in 2025
- Comparing the Core: What Each Field Truly Focuses On
- Course Curriculum Breakdown: What One Will Actually Study in Biomedical Engineering vs Biotechnology
- Where One Will Learn: Labs, Classrooms, and Cross-Disciplinary Exposure
- Skills That Set You Apart: Not Just What You Know, But How You Apply It
- Career Paths, Industry Applications, and How Each Field Evolves Over Time
- Recruiter Insights: What Employers Look for in Fresh Graduates
- Global Employability: Which Field Makes You Borderless?
- Future Trends and Ethical Considerations
- How to Choose: A Decision Guide for Students
- Your Path to Global Biotech Careers Starts at Shiv Nadar University (Institution of Eminence)
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Biomedical Engineering vs Biotechnology Comparison Matters More than Ever in 2025
Many students finishing Class 12 stand at crossroads. They’ve excelled in Biology, Physics, Chemistry, and now they need to decide: biomedical engineering vs biotechnology.
The confusion is organic.
What sounds alike at first glance often leads to entirely different futures. Pick biotechnology, and one could end up working on gene-edited seeds. Pick biomedical engineering, and one might be designing the next MRI scanner.
Parents ask, “Which one offers better job security?” Students wonder, “Do I need to love coding for either?” Institutes throw around big words like “interdisciplinary” and “lab-intensive,” but rarely explain what that means in plain terms.
This blog breaks that down clearly.
It explains what each path offers, how they differ, and what recruiters are actually looking for in 2025. It’s designed to help one make a confident, informed choice.
This is not just another academic debate. It's a decision that shapes careers, incomes, job satisfaction, and even the kind of impact one has on society.
Comparing the Core: What Each Field Truly Focuses On
Understanding the heart of each subject is the first step in this biomedical vs biotechnology comparison.
Here’s how the core of these two fields differ:
|
Parameter |
Biotechnology |
Biomedical Engineering |
|
What it deals with |
Living systems and how to use them in areas like food, pharma, and agriculture |
Engineering and tech used in medicine and hospitals |
|
Where it applies |
Industries: agriculture, pharma, environment |
Sectors: hospitals, med-tech companies, diagnostics |
|
Example from competitors |
Creating pest-resistant cotton |
Building imaging tools like CT scans |
Biotechnology leans towards biology + chemistry + application. Biomedical engineering leans towards maths + mechanics + healthcare design.
In biotechnology, one works with cells, bacteria, or DNA. In biomedical engineering, one works with machines, devices, and systems that help doctors and patients.
Course Curriculum Breakdown: What One Will Actually Study in Biomedical Engineering vs Biotechnology
The syllabus in both fields has science at its base. But the subjects, teaching style, and skills picked up are quite different.
Biotechnology Syllabus Highlights
- Microbiology
- Biochemistry
- Genetic Engineering
- Molecular Biology and
- Bioinformatics
Practical focus:
Hands-on lab work with DNA, cell cultures, and enzymes.
Specializations offered:
Pharmaceutical biotechnology, agricultural biotech, and plant genetics.
Biomedical Engineering Syllabus Highlights
- Engineering Mechanics
- Biomaterials
- Medical Imaging
- Biomechanics and
- Systems Physiology
Practical focus:
Design projects, CAD software training, and hardware prototyping.
Specializations offered:
Medical robotics, bio-instrumentation, and tissue engineering.
Where One Will Learn: Labs, Classrooms, and Cross-Disciplinary Exposure
The way knowledge is delivered matters just as much as the subjects themselves. Here’s what the learning environment looks like in both fields.
Biotechnology Program
- Work is mainly in wet labs
- Daily interaction with microscopes, pipettes, centrifuges
- Experiments on DNA extraction, cloning, fermentation, etc.
- Long hours in research settings, often in lab coats
Biotech students often take part in field visits to pharmaceutical plants or agri-bio stations. This connects theory to industry needs.
Biomedical Engineering Program
- Classrooms combine engineering labs and hospitals
- Practical training on simulation software and medical imaging systems
- Final-year projects often involve designing medical devices
Biomedical students may get access to projects like 3D-printed prosthetics or brain-machine interfaces. This isn't just engineering. It’s problem-solving for the human body.
In Summary:
- Biotechnology = lab-heavy + biology-focused
- Biomedical = design-heavy + tech-focused
That’s where the real divide is. It’s not just about science; it’s about what kind of problems one wants to solve.
Skills that Set You Apart: Not just what You Know, but how You Apply it
Key Skills for Biotechnology Students
- Molecular biology and genetics
- Bioinformatics
- Microbiology
- Biochemistry
- Lab skills for culturing and manipulating cells
- Gel electrophoresis, spectrometry
- Data analysis tools (SPSS, R, Excel)
- Computational tools
- Research writing and documentation, and
- Understanding regulatory norms in pharma and agriculture
Key Skills for Biomedical Engineering Students
- CAD design (AutoCAD, SolidWorks)
- Medical imaging knowledge (MRI, CT tools)
- Knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and materials science
- Proficiency in biomedical instrumentation
- Creativity in generating innovative solutions for healthcare challenges
- Embedded systems and electronics basics
- Clinical safety and compliance protocols, and
- Project design and device prototyping
Technical Tools Used in Each Field
|
Skill Type |
Biotechnology |
Biomedical Engineering |
|
Lab Tools |
Microscopes, Centrifuges, DNA Kits |
ECG, Spirometers, Bio-sensors |
|
Software |
BioEdit, BLAST, BioPython |
MATLAB, Arduino, LabVIEW |
|
Hardware |
Bioreactors, Spectrophotometers |
Prosthetic limbs, MRI-compatible tools |
|
Common Projects |
Drug formulation, gene cloning |
Design of wearable devices, rehabilitation systems |
Career Paths, Industry Applications, and how each Field Evolves over Time
When comparing biomedical engineering vs biotechnology, the biggest difference is in where one ends up working.
Biotechnology Careers
- Research Scientist
- Quality Control Analyst
- Bioprocess Engineer
- Agricultural Biotechnologist
- Biotech Analyst
- Biochemist
- Epidemiologist
- Bioinformatics Specialist
- Genetic Counselor and
- Biotech Consultant
Top recruiters:
Biocon, Serum Institute of India, Syngene, and Monsanto
Biomedical Engineering Careers
- Clinical Engineer
- Medical Device Designer
- Regulatory Affairs Officer
- R&D Engineer
- Biomedical Scientist/Researcher
- Biomaterials Developer
- Biomechanical Engineer and
- Biomedical Device Engineer
Top recruiters:
Siemens Healthineers, Philips, GE Healthcare, and Medtronic
|
Factor |
Biotechnology |
Biomedical Engineering |
|
Industry Type |
Pharma, Agri, Research |
Hospitals, MedTech, Robotics |
|
Work Environment |
Labs, Fields, Research |
Hospitals, Labs, Manufacturing |
|
Technical Focus |
Genetics, Molecules |
Electronics, Mechanics |
|
Tools Used |
DNA sequencers, Bioreactors |
ECG, CAD, 3D Printers |
So the debate of biomedical vs biotechnology isn’t about which one is better. It’s about what kind of problems one wants to solve: public health, hospital innovation, food supply, or disease control.
Recruiter Insights: What Employers Look for in Fresh Graduates
Degrees open doors. Skills and experience keep them open. In both biomedical vs biotechnology, recruiters want one thing: candidates who can work independently on real problems.
For biotechnology, the ideal candidate is someone with a sharp eye for data, strong wet-lab discipline, and basic awareness of pharma regulations. For the biomedical field, graduates who can think like engineers and still understand a hospital’s needs are in high demand.
What they Prefer across Both Fields:
- Final-year internships in a real lab or hospital setting
- Familiarity with industry tools, software, and machines
- Communication skills for writing reports, not just passing exams
- Certifications
The job market isn’t short of degrees. It’s short of doers. The more real-world experience one adds, such as summer internships, workshops, and industry projects, the stronger the profile.
Global Employability: Which Field Makes You Borderless?
Biotech is Research-Heavy and Globally Scalable
- High demand in pharma, food safety, and genetics
- Career paths in Europe, the US, Singapore, Australia
- Popular roles: Research associate, product development lead, regulatory officer
Biomedical Engineering is Regulated but Expanding
- Strong in developed healthcare systems
- Work in hospitals, diagnostics, medical robotics
- High in demand across the US, UK, Germany, Canada
A biotech degree gives flexibility across industries. Biomedical fits better where healthcare tech is growing fast.
Future Trends and Ethical Considerations
When one thinks long-term, the biomedical engineering vs biotechnology question goes beyond careers. It’s about impact. It’s about how science meets humanity.
Biotechnology Trends to Watch
CRISPR and Gene Editing:
Editing genes to cure diseases is no longer science fiction. But it raises ethical concerns: should one alter DNA before birth?
Synthetic Biology:
Creating life-like cells in labs. Can they solve food or energy crises?
Green Biotech:
Eco-friendly fertilizers and biofuels. But are they scalable?
Bioinformatics and AI:
Tools to predict drug success and genome behaviour.
Biomedical Engineering Trends that Matter
Wearable Health Devices:
Think smart watches that track blood pressure in real-time.
Tissue Engineering:
Lab-grown skin, organs, and bones that reduce the need for donors.
Neural Implants and Brain Interfaces:
Helping paralysed patients move robotic limbs with thought. Also raises privacy and ethical concerns.
Medical Robotics:
Surgical bots that reduce error, but also need tight regulation.
Ethical Considerations
Biotech:
- Who owns modified genes?
- What are the side effects of editing crops or humans?
Biomed:
- What happens if a device fails inside a patient?
- How do companies ensure fair access to expensive tools?
How to Choose: A Decision Guide for Students
If the biomedical engineering vs biotechnology debate still feels cloudy, let’s simplify it. Ask these 5 questions:
Do you enjoy designing machines or studying living cells?
- Design → Go biomedical
- Living cells → Go biotech
Are you better at maths or biology?
- Maths → Favor biomedical
- Biology → Favor biotech
Do you see yourself in a hospital or in a research lab?
- Hospital → Biomedical
- Lab → Biotechnology
Are you interested in pharma/agriculture or medical devices?
- Pharma/Agri → Biotech
- Devices → Biomed
Do you want to build tools or study organisms?
- Tools → Biomedical
- Organisms → Biotechnology
|
Preference Type |
Choose Biotechnology If |
Choose Biomedical Engineering If |
|
Subject Strength |
Strong in biology |
Strong in maths and physics |
|
Career Goal |
Research, pharma, agri |
Hospitals, medical tech, diagnostics |
|
Job Environment |
Research labs, factories |
Clinics, med-device firms, R&D labs |
|
Tools Used |
Pipettes, gene sequencers |
ECG, prosthetics, 3D modellers |
|
Mindset Fit |
Curious about life forms |
Curious about health technology |
No field is better. It’s about fit. One person’s perfect career could be another’s daily struggle. The goal is to match natural skills and interests with the demands of the field.
Your Path to Global Biotech Careers Starts at Shiv Nadar University (Institution of Eminence)
At Shiv Nadar University, the B.Sc. (Research) in Biotechnology isn’t taught in isolation. It’s part of a broader ecosystem where biology, chemistry, computing, and critical thinking are woven together to prepare students for the evolving demands of science and society.
Offered under the Department of Life Sciences within the School of Natural Sciences, this B.Sc. Biotechnology program is built for those who see science not just as a subject but as a tool for change. Here’s what sets it apart:
- Recognized as an Institution of Eminence by the Government of India
- 3+1-year undergraduate program aligned with the National Education Policy
- Features state-of-the-art teaching and research laboratories.
- Faculty from leading institutions in India and worldwide
- Hosts two specialized research centers.
- Vibrant community with numerous extracurricular activities
- The "Opportunities for Undergraduate Research" (OUR) program fosters a research-oriented atmosphere for undergraduate students and
- Curriculum with a strong balance of theoretical knowledge and practical application.
For students who want to grow into thoughtful scientists, capable in both lab and life, the B.Sc. (Research) in Biotechnology at Shiv Nadar University is a compelling, future-ready choice.
Conclusion
Choosing between biomedical engineering vs biotechnology is not about which is better; it’s about which suits one's strengths, goals, and mindset. While biomedical focuses on building healthcare technologies, on the other hand, biotechnology is rooted in biology and research-driven innovations.
If you're looking for a program that encourages innovation, values research from day one, and connects you to a broader world of scientific opportunity, Shiv Nadar University’s B.Sc. (Research) in Biotechnology offers a solid academic and practical foundation to get started.
FAQs
Is biotechnology or biomedical engineering more employable in India or abroad?
Biomedical has more roles in India currently; biotech has stronger global research demand.
Can biomedical engineers do without maths?
No, Maths is a very important integral part of biomedical engineering.
What factors should I consider when deciding between pursuing a career in biotechnology or biomedical engineering?
When choosing between biotechnology and biomedical engineering, some key factors you need to consider are personal interests, career goals, preferred industry sectors, job prospects, and salary potential.